Blood glucose and blood sugar are interchangeable terms, and both are crucial to the health of the body; especially for people with diabetes.
Most diabetics will be familiar with the terms blood glucose, blood glucose test, blood glucose level and blood glucose meter, but what does blood glucose really mean? Why do blood sugar levels need to be controlled?
What are blood glucose levels?
Blood sugar levels are literally the amount of glucose in the blood, sometimes called the serum glucose level. Usually, this amount is expressed as millimoles per litre (mmol/l) and stay stable amongst people without diabetes at around 4-8mmol/L.
Spikes in blood sugar will occur following meals, and levels will usually be at their lowest in the early mornings. When it comes to people with diabetes,
blood sugar fluctuates more widely.
Blood Glucose Guides:
Why do blood glucose levels need to be controlled?
High levels of glucose present in the blood over a sustained period of time end up damaging the blood vessels. Although this does not sound too serious, the list of resultant complications is.
Poorly controlled blood glucose levels can increase your chances of developing diabetes complications including nephropathy, neuropathy, retinopathy and cardiovascular diseases.
The time-scale for the development of these complications is usually years, but be aware that type 2 diabetes is often not diagnosed until a relatively late stage.
How do I find out what my blood glucose levels are?
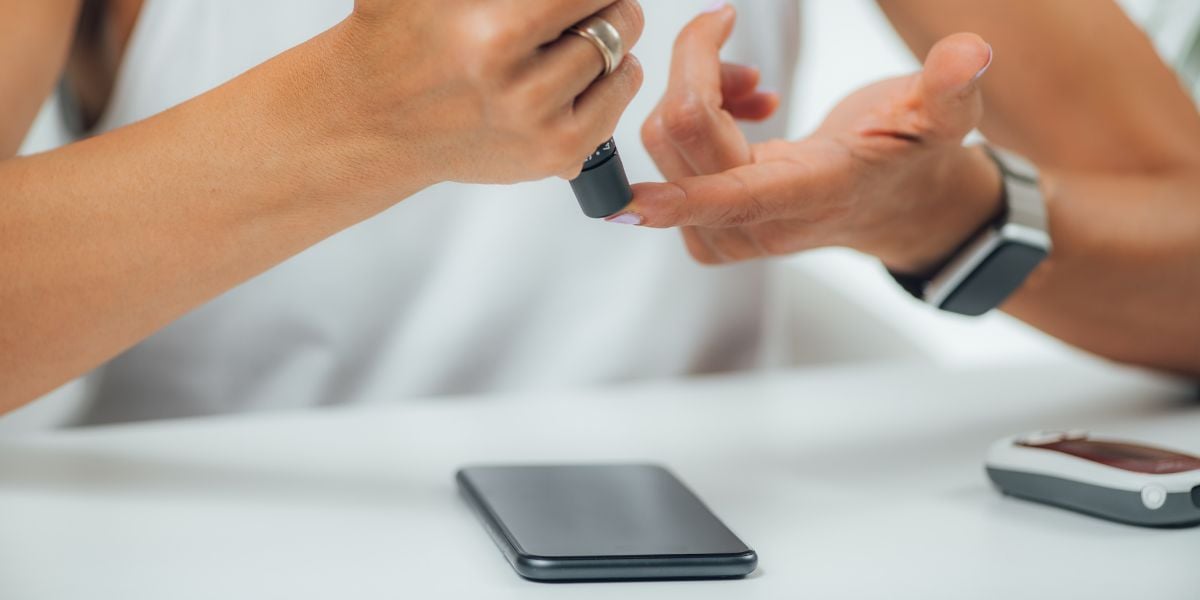
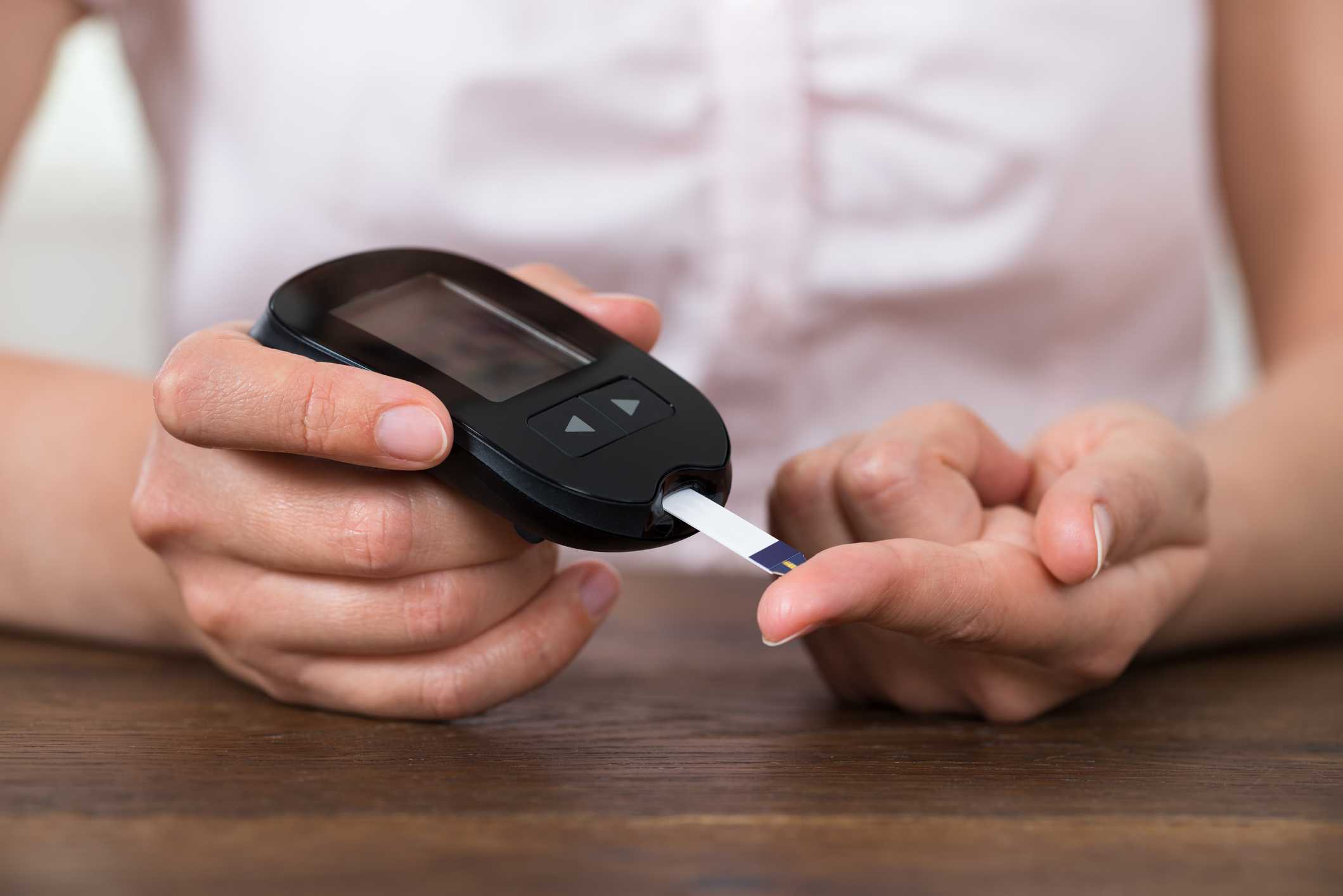
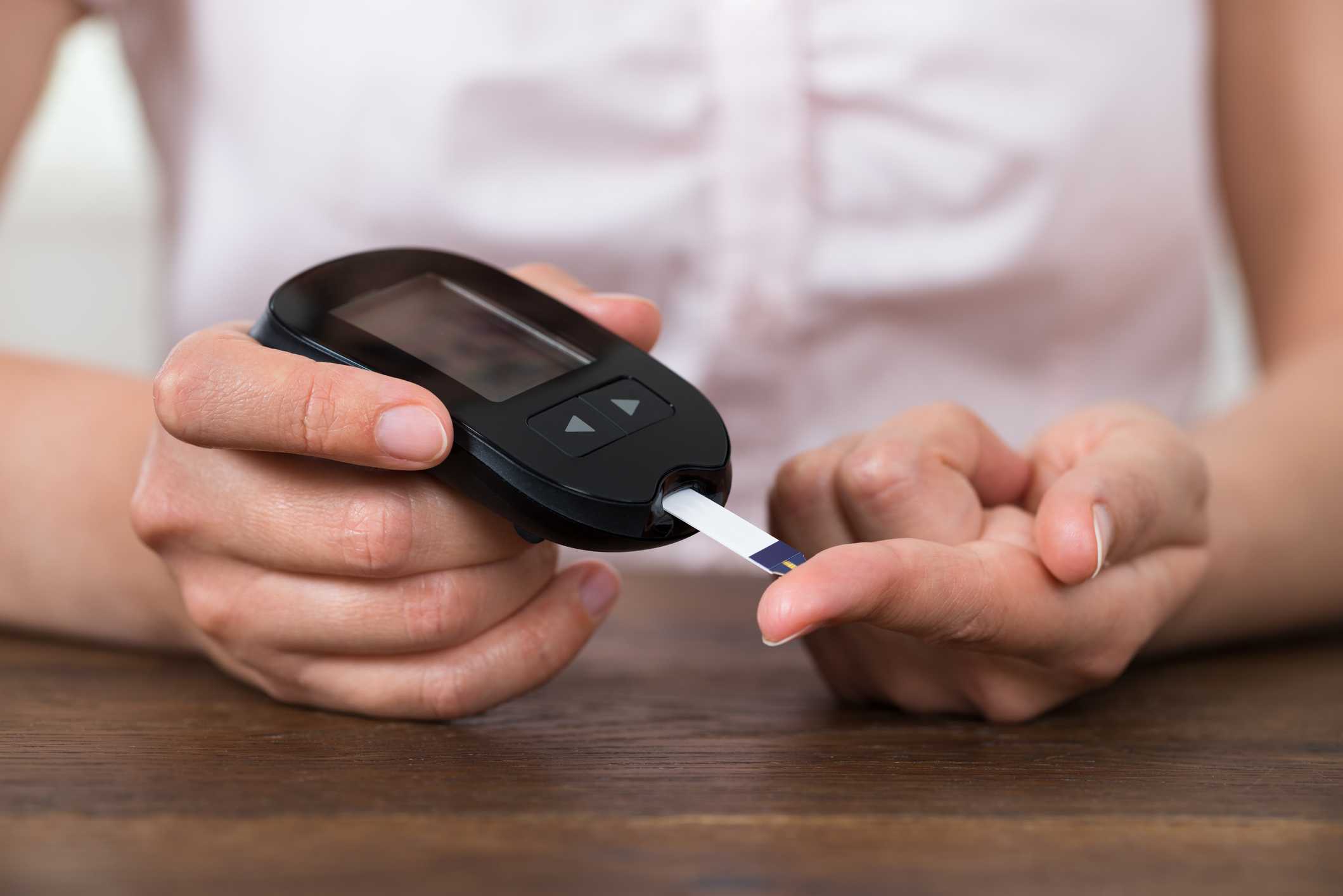
You can use home testing kits, although before doing so read our guide to blood glucose monitors.
Measure levels by putting a drop of blood on a strip and placing it into a BGM (blood glucose meter). Prick your finger with a specially designed lancet to draw blood.
What is a good blood glucose level?
NICE guidelines for the UK currently recommend the following:
- A normal pre-prandial (before meal) blood glucose level will be between 4 and 7 mmol/l.
- Aftereating (post-prandial) levels should be below 9 mmol/l when tested 2 hours after a meal.
- When going to bed for the night, levels should be no more than 8 mmol/l.
When should blood glucose levels be measured?
The number of times per day blood glucose levels should be measured depends entirely on the diabetics. Type 1 diabetics using insulin should check their blood sugar levels before every meal, sometimes as often as five times per day.
For type 2 diabetics controlling their condition with diet, you should test several times a week.
However, this doesn’t apply to everyone, and each individual case should seek expert advice.
Are there special times when blood glucose should be measured?
Any time you feel ill, and over time if you can feel your blood sugar becoming too low or too high, you should check your blood glucose levels.
You should also be aware that a reading over 20mmol/l should prompt a urine test for the presence of ketones
What is an HbA1c test and how does it relate to blood glucose?
HbA1c tests show average blood glucose levels over a sustained period of time. HbA1c is glycated haemoglobin and more of it is produced in the body by high blood glucose levels.
Different scores of HbA1c show good, fair, poor and bad control of diabetes. Increasing HbA1c levels indicate greater risk of complications.